Mar 14, 14 · MicroRNAs (miRNAs) bind to mRNAs and target them for translational inhibition or transcriptional degradation It is thought that most miRNAmRNA interactions involve the seed region at the 5′ end of the miRNA The importance of seed sites is supported by experimental evidence, although there is growing interest in interactions mediated by the central region of the miRNASOFTWARE Open Access Online GESS prediction of miRNAlike offtarget effects in largescale RNAi screen data by seed region analysis Bahar Yilmazel1, Yanhui Hu1, Frederic Sigoillot2, Jennifer A Smith3, Caroline E Shamu3, Norbert Perrimon1,4 and Stephanie E Mohr1* AbstractIn molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codonThe 3′UTR often contains regulatory regions that posttranscriptionally influence gene expression During gene expression, an mRNA molecule is transcribed from the DNA sequence and is later translated into a protein
Mirepress Modelling Gene Expression Regulation By Microrna With Non Conventional Binding Sites Scientific Reports
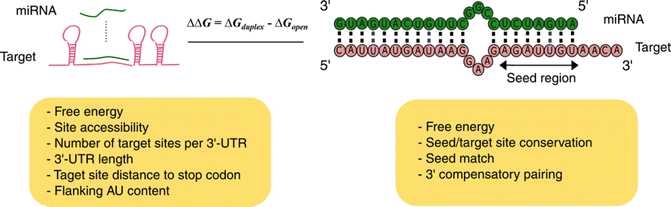
Seed region of mirna
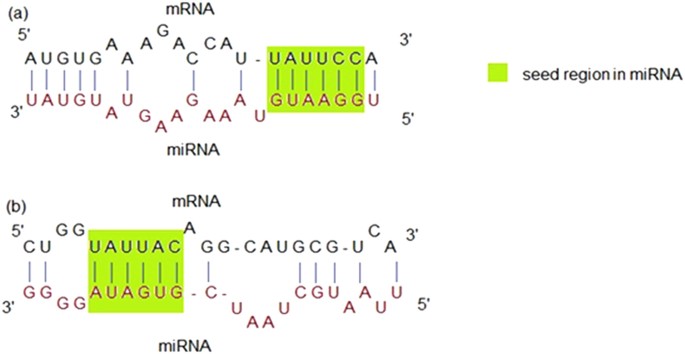
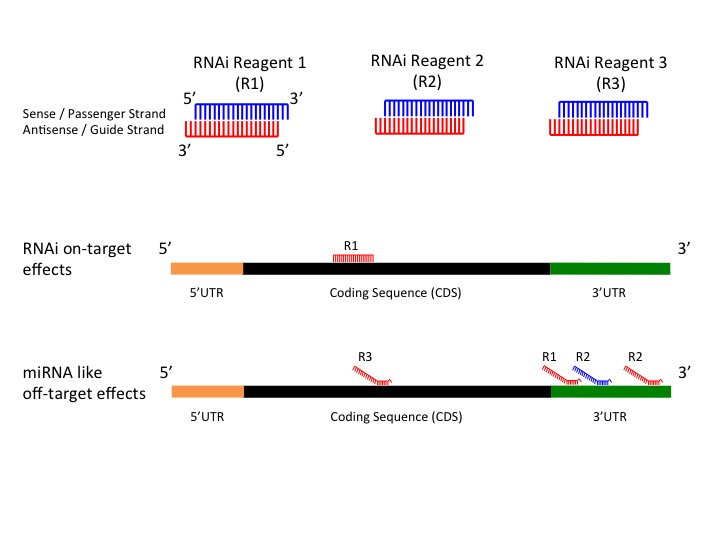
Seed region of mirna-Canonically, miRNA targeting is reliant on base pairing of the seed region, nucleotides 2–7, of the miRNA to sites in mRNA 3′ untranslated regions Recently, the 3′ half of the miRNA has gained attention for newly appreciated roles in regulating target specificity and regulationSense strand), also called the 'seed region', is complementary to the 3′ untranslated regions (UTRs) of multiple mRNAs, causing degradation of their associated transcripts 8,9 To improve the interpretation of RNAi datasets and to help minimize followup experimental efforts, it is important to identify transcripts that are



1
TargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA (Lewis et al, 05) As an option, predictions with only poorly conserved sites are also providedMay 26, 17 · Bases 2–8 (seed region) from the 5′end of the mature miRNA are critical determinants of target complementarity 22 Premature forms of a miRNAMicroRNAs (miRNAs) are key regulators of sequencespecific gene silencing However, crucial factors that determine the efficacy of miRNAmediated target gene silencing are poorly understood Here we mathematized basepairing stability and showed that miRNAs with an unstable 5′ terminal duplex and stable seedtarget duplex exhibit strong silencing activity
Dec 24, 14 · Part of a miRNA is a 2–8base pair long seed region in their 5′ end The interaction happens between these seed regions and complementary "seed matches" on the target sites of the mRNAs 7TargetScan does its own classification of miRNAs into families, based on identical seed region, so miRNA family classification and, even more likely, nomenclature can differ between these databases In TargetScan 5 Custom, nonconserved target sites are not shown;A mismatch tolerance test assay, based on pools of transgenic strains, revealed that target hybridization to nucleotides of the seed region, at the 5′ end of an miRNA, was sufficient to induce moderate repression of expression In contrast, pairing
The latest version of this resource was released in August 15 miRSearchMiRNAs regulate the gene expression by binding to the mRNA The seed sequence is essential for the binding of the miRNA to the mRNA The seed sequence or seed region is a conserved heptametrical sequence which is mostly situated at positions 27 from the miRNA 5´end Even though base pairing of miRNA and its target mRNA does not match perfect, the "seed sequence"TargetScan predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of 8mer, 7mer, and 6mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA As an option, only conserved sites are predicted Also identified are sites with mismatches in the seed region that are compensated by conserved 3' pairing and centered sites




Mismatches In The Mirna Proximal Seed Region Disrupt The Binding Download Scientific Diagram



Cells Free Full Text The Butterfly Effect Of Rna Alterations On Transcriptomic Equilibrium Html
Dec 11, 15 · Specifically, 2 nd to 7 th /8 th nt in the 5' region (seed region) of siRNA recognises the unintended target gene within the 3'UTR of mRNA sequence (Fig 1C) 10Jan 01, 18 · Our results demonstrate that SNPs in clustered miRNA seed regions can take part in more intricate generegulating networks with lower functional cost by functional complementarity 2 Materials and Methods 21 GenomeWide Identification of SNPs in Human miRNA Seed RegionsThe members of a same miRNA may differ in the seed region and even one basepair difference between them can change their interaction with the target



Microrna Computational Prediction And Analysis Ppt Download




Frontiers In Bioscience 17 2508 2540 June 1 12 Micrornas Molecular Features And Role In Cancer Elodie Lages1 2 Helene Ipas1 2 Audrey Guttin1 2 3 Houssam Nesr1 2 Francois Berger1 2 Jean Paul Issartel1 2 3 4 1inserm U6 Team7
In human miRNA seed regions A total of 1879 SNPs were mapped to 1226 human miRNA seed regions We found that miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region are significantly enriched in miRNA clusters We also found that SNPs in clustered miRNA seed regions have a lower functional effect than have SNPs in nonclustered miRNA seed regions Additionally, weApr 27, · To characterize the basepairing patterns of miRNAtarget interaction, we searched for overrepresented sequence elements in all the targets discovered for each miRNA For most of the top expressed miRNAs, highly enriched sequence motifs emerged as complementary to the extended miRNA seed region (nucleotides 1–8 of miRNA) (Fig 4A and S7 Fig)MiRNA seed region is more critical than the 3′ region for target recognition in A thaliana (Mallory et al, 04) Moreover, plant and algal small RNAs also induce translational repression of perfectly complementary target mRNAs without, or with only minimal, transcript destabili
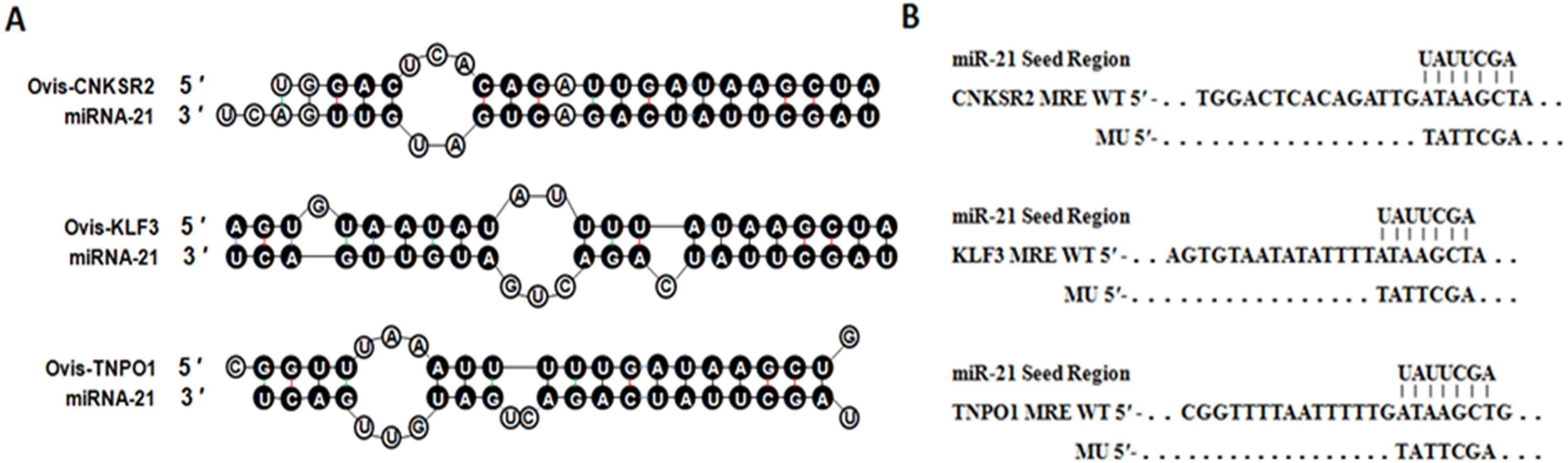



Identification Of Microrna 21 Target Genes Associated With Hair Follicle Development In Sheep Peerj




Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html
The most critical region for complementarity is the seed region (nucleotides 2–7 from the 5'terminus of the miRNA) 4,7 Aside from the seed region, other criteria have been established that can enhance miRNAmediated repression including complementarity at position 8 and the presence of an adenosine residue opposite the first miRNA nucleotide 8,9 Any polymorphism thatMicroRNA Editing in Seed Region Aligns With Cellular Changes in Hypoxic Conditions PubMed RNA editing is a finely tuned, dynamic mechanism for posttranscriptional gene regulation that has been thoroughly investigated in the last decadeComplementarity to an miRNA Seed Region Is Sufficient to Induce Moderate Repression of a Target Transcript in the Unicellular Green Alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Tomohito Yamasaki,1 Adam Voshall,2 EunJeong Kim,2 Etsuko Moriyama,2 Heriberto Cerutti,2 and Takeshi Ohama1 1




Miraw A Deep Learning Approach To Predict Mirna Targets By Analyzing Whole Mirna Transcripts Biorxiv




Different Seed Match Regions Of Mirnas Mirnalyze Follows A Download Scientific Diagram
TargetScan is a target prediciton tool that predicts biological targets of miRNAs by searching for the presence of conserved 8mer and 7mer sites that match the seed region of each miRNA The target prediction software is frequently updated;Aug 02, 16 · One class of pattern consists of perfect WatsonCrick binding at the 5'end of the miRNA This region is known as "seedregion" and found at the 27 base of the miRNA This region is able to suppress the target mRNAs without having a complete base pairing atFor miRNAs with low GC content of the seed region, noncanonical targeting was the dominant mechanism for target recognition In contrast to canonical targeting, noncanonical targeting did not lead to significant target downregulation at either the RNA or protein level




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science




Microrna Wikipedia
Apr 22, 16 · miRNA seed region enrichment in the exosomal lncRNA is independent of sequence length To investigate if sequence length was a determinant in miRNA seed enrichment, we compared the average length of all exosomal lncRNAs to the cellular lncRNAs in each cell lineSCIENTIFIC REPORTS srep 1 wwwnaturecomscientificreports Long noncoding RNAs harboring miRNA seed regions are enriched in prostate cancer exosomes Alireza Ahadi1,2, Samuel Brennan3, Paul J Kennedy2,4, Gyorgy Hutvagner2 & Nham Tran2,5 Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) form the largest transcript class in the human transcriptomeAfter the siRNA seed region anneals, the catalytic RNase H domain of Argonaute then subjects perfectly complementary mRNA sequences 10 nucleotides from the 5' end of the incorporated siRNA strand to nucleolytic degradation, resulting in the translational inhibition of the target mRNA




Snps In Microrna Target Sites And Their Potential Role In Human Disease Open Biology




Rna Interference The Molecules That Govern Genetic Control Young Scientists Journal
Jan 22, 19 · The impact of miRNA seed types on target downregulation Previous studies have identified several major types of canonical miRNA target sites, including those matching to the 6mer, 7mer, or 8mer miRNA seed sequences (Table 2)Sequence conservation analysis suggested that target sites pairing to longer miRNA seeds are more conserved across species and thus areI microRNA si appaiano all'mRNA target attraverso i nucleotidi 28 del miRNA (seed region) e il sito complementare della regione 3'UTR dell'mRNA bersaglio PDF PDFDec 29, 11 · An SNP in the premiRNA region of hsamir499 (rsA>G) Song et al evaluated the SNP (rs) within the miR502 seed binding region in the 3′UTR of the SET8 gene in a casecontrol study on 1110 breast cancer cases and 1097 controls




Not Mir Ly Small Rnas Big Potential For Micrornas In Therapy Journal Of Allergy And Clinical Immunology
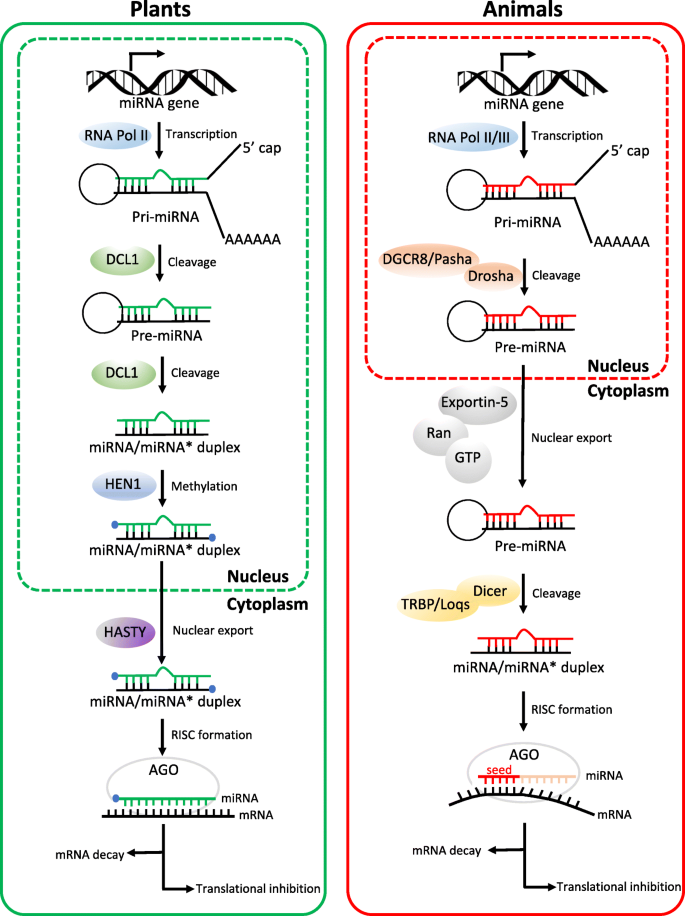



Micrornas From Plants To Animals Do They Define A New Messenger For Communication Nutrition Metabolism Full Text
Reveal that miRNA containing inosine in the seed region exhibits a different degree of silencing efficiency compared to the corresponding miRNA with guanosine at the same position The difference in basepairing stability, deduced by melting temperature measurements, between seedtarget duplexes containing either CG or IC pairs may account forOct 15, 13 · Base pairing of the miRNA seed region (positions 2–8 from the 5′ end of an miRNA) in animals is critical for target recognition and repression (Bartel, 09;The seed regions are regions present within the miRNA binding regions Although there are several factors that pave a way to the binding between miRNA and mRNA, the impact of binding is determined by the seed sequence within the miRNA The seed region consists of a continuous string of at least 6 to 8 nucleotides miRNA recognizes its target by
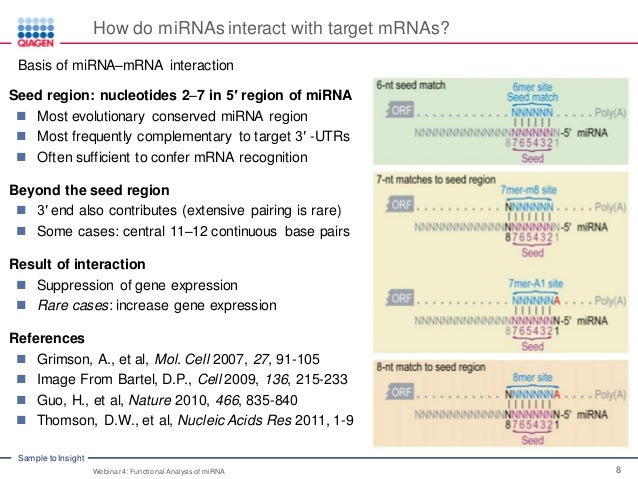



Functional Analysis Of Mirna Mirna And Its Role In Human Disease Web




Helix 7 In Argonaute2 Shapes The Microrna Seed Region For Rapid Target Recognition The Embo Journal
Dec 18, 12 · Furthermore, we evaluated the silencing efficiencies of miRNAs with the same seven nucleotide compositions in their seed regions (A = 3, U =MicroRNAs, or miRNAs, posttranscriptionally repress the expression of proteincoding genes The human genome encodes over 1000 miRNA genes that collectively target the vast majority of messenger RNAs (mRNAs) Basepairing of the socalled miRNA "seed" region with mRNAs identifies many thousands of putative targetsFor the 1226 human miRNAs with SNPs in their seed region, 314 (256%) of them are located in miRNA clusters, whereas among the 1587 human miRNAs without SNPs in their seed region, only 3 (2%) of them are located in miRNA clusters (P = 606 × 10 −4, χ 2 test) (Table S2) miRNAs from the same cluster have the tendency to regulate the




Snps In Microrna Target Sites And Their Potential Role In Human Disease Open Biology
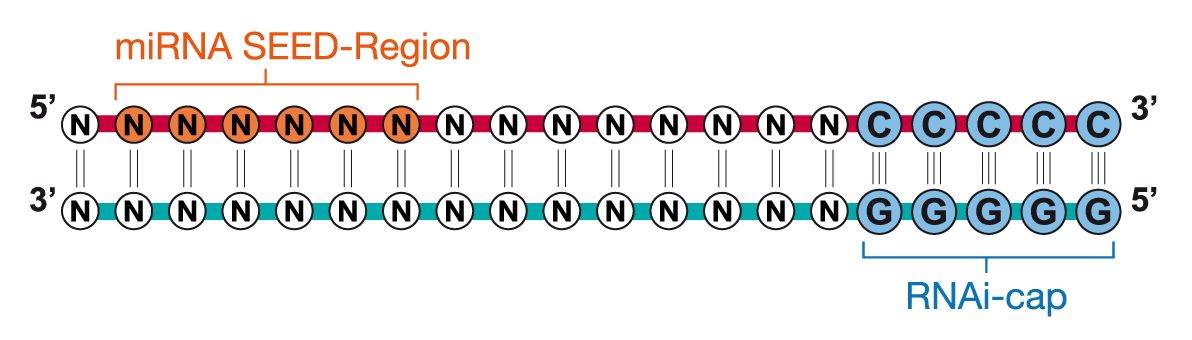



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna
And some miRNA nucleotides are more important than others (8, 9) Specifically, pairing to the miRNA "seed region" (nt 2 to 7 or 2 to 8, from the 5′ end) is the most evolutionarily conserved feature of miRNA targets in animals (10–14) Crystal structures of human Argonaute proteins show nt 2 to 6 of the guide RNA bound1–5, and basepairing stability between the seed region and target mRNA, miTm 2–8 The following formula should appropriately predict miRNAmediated genesilencing efficacy Tm 2–8 2 053 3However, this information is available for annotated miRNAs




Sites Matching In The Mirna Seed Region Including All K Mer 8mer Download Scientific Diagram



1
Oct , 16 · The miRNA sequence can be separated into five functional domains that affect miRNAtarget recognition 5′ anchor (nt 1), seed sequence (nts 2–8), central region (nts 9–12), 3′ supplementary region (nts 13–16), and 3′ tail (nts 17–22) (Wee et al, 12) We anticipated that complementarity to the seed sequence of the cognate miRNA would be a prominent feature inAtoI editing in the miRNA seed region regulates target mRNA selection and silencing efficiency 11 Pages AtoI editing in the miRNA seed region regulates target mRNA selection and silencing efficiency Nucleic acids research, 14 Josephine Galipon Download PDFApr 01, · In contrast to the miRNA 5′ (seed) region, the role of the 3′ region in miRNAtarget recognition is less defined Early evidence arose from reported cases of miRNA repression without perfect pairing in the seed region 13 In those cases, increased pairing in the 3′ region was observed (Fig 1 B)



Www Heartlungcirc Org Article S1443 9506 11 5 Pdf
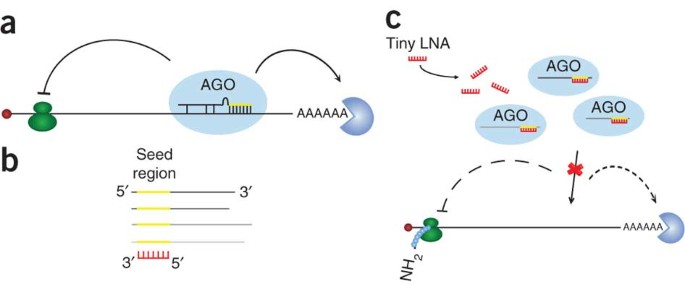



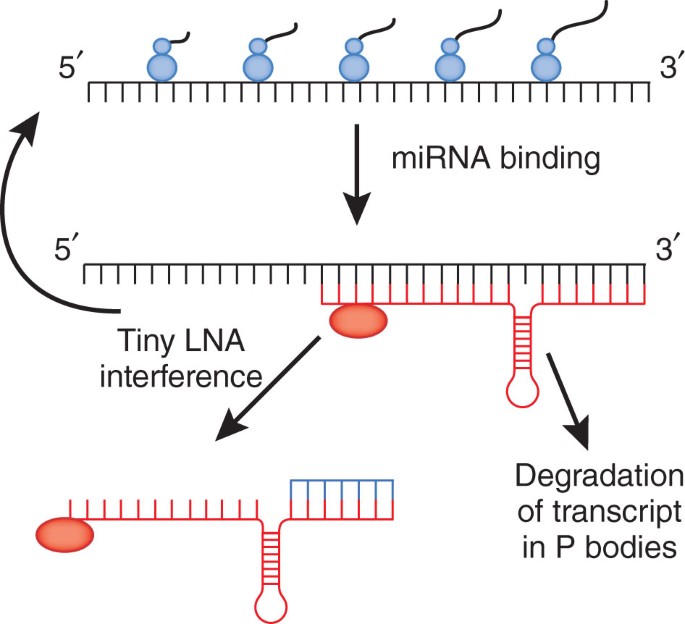
Silencing Of Microrna Families By Seed Targeting Tiny Lnas Nature Genetics
Pasquinelli, 12) In contrast, most evidence indicates that miRNAs in land plants require more extensive pairing to their targets (Schwab et al , 05 ;




Miraw A Deep Learning Approach To Predict Mirna Targets By Analyzing Whole Mirna Transcripts Biorxiv




Tiny Giants Of Gene Regulation Experimental Strategies For Microrna Functional Studies Steinkraus 16 Wires Developmental Biology Wiley Online Library




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Figure 16 From Microrna Function Detection And Bioanalysis Semantic Scholar



Principles Of Microrna Target Recognition



Miraw A Deep Learning Based Approach To Predict Microrna Targets By Analyzing Whole Microrna Transcripts



New Insights Into The Function Of Mammalian Argonaute2




A Cartoon Showing The Site And Mechanism Of Mirna Targeting To Mrna Download Scientific Diagram



Computational And Experimental Identification Of Tissue Specific Microrna Targets Springerlink




Stability Of Mirna 5 Terminal And Seed Regions Is Correlated With Experimentally Observed Mirna Mediated Silencing Efficacy Topic Of Research Paper In Biological Sciences Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On




Clustering Pattern And Functional Effect Of Snps In Human Mirna Seed Regions




Rna Mrna Target Interaction Schematic Overview Of A Mirna Interaction Download Scientific Diagram




Microrna Regulation And Cardiac Calcium Signaling Circulation Research
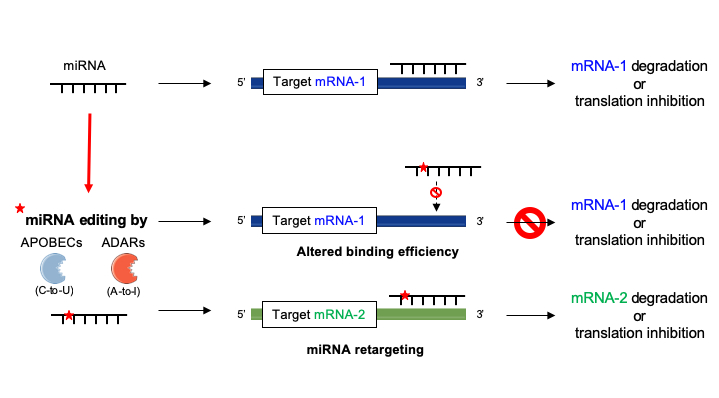



Ijms Free Full Text Deciphering Mirnas Action Through Mirna Editing Html




Introduction To Microrna Programmer Sought




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Biorxiv



Stopping Rna Interference At The Seed Nature Genetics



1



Mirnas As Novel Biomarkers For Bone Related Diseases Foessl Journal Of Laboratory And Precision Medicine




Chemical Modifications In The Seed Region Of Mirnas 221 222 Increase The Silencing Performances In Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumor Cells Sciencedirect
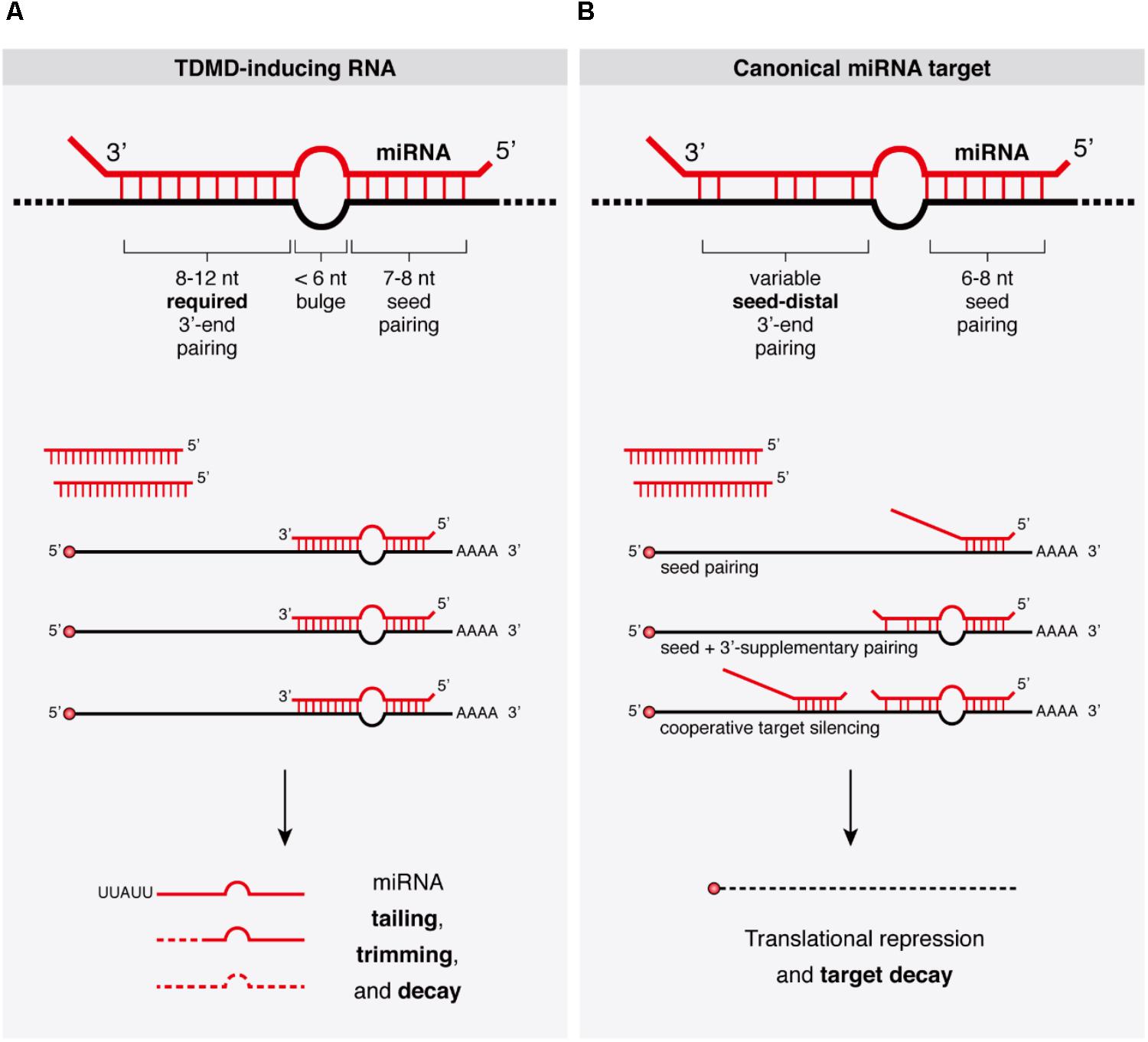



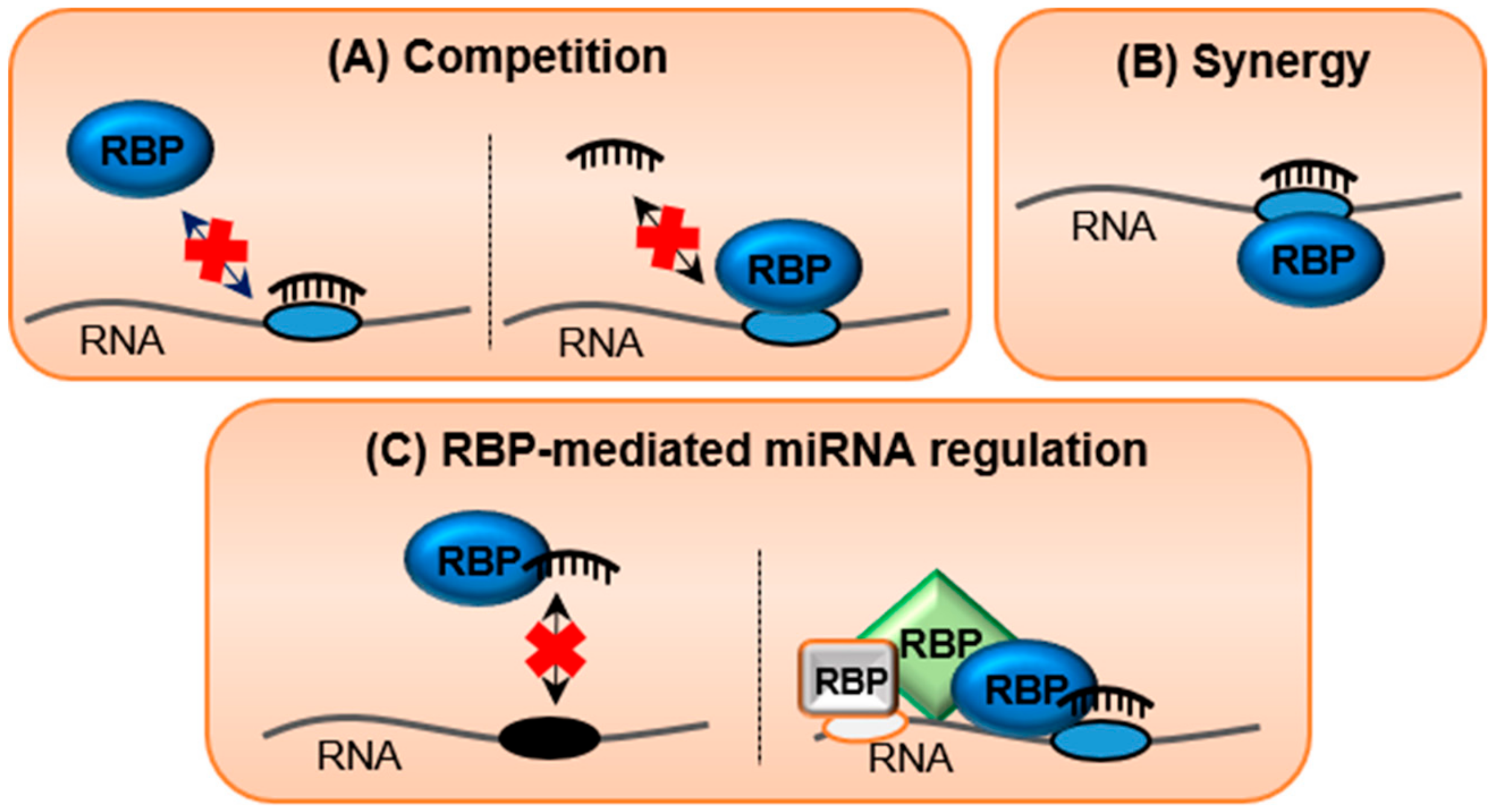
Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal



Targetscan Non Canonical Sites



Microrna Wikipedia
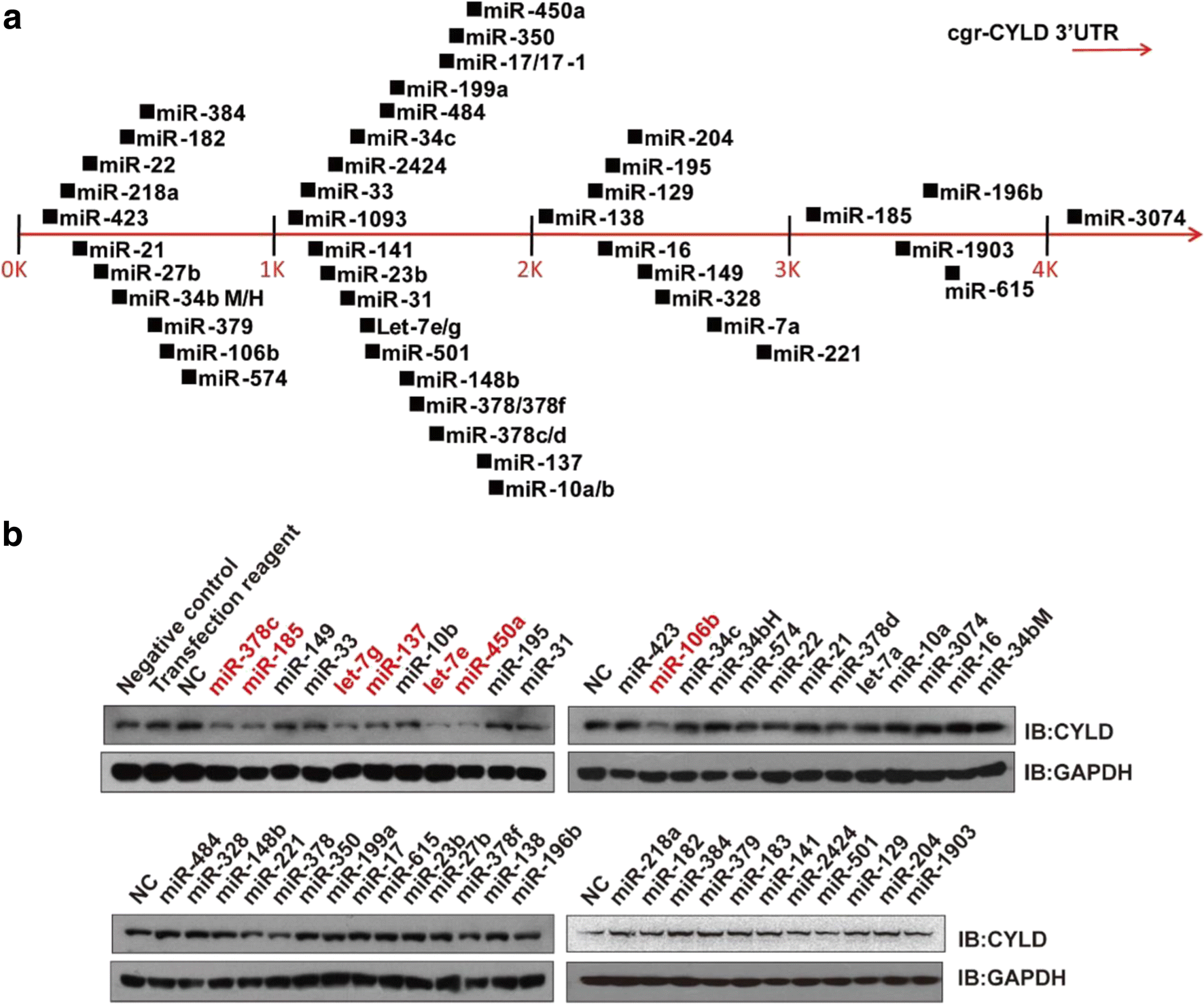



Figure 1 Mir 106b Promotes Therapeutic Antibody Expression In Cho Cells By Targeting Deubiquitinase Cyld Springerlink
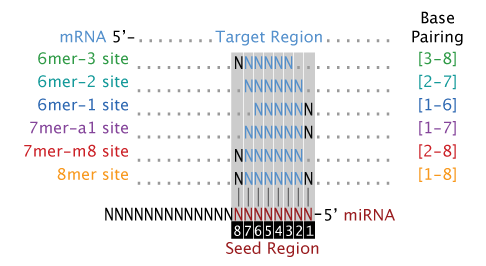



Mirvestigator Framework Detect The Mirnas Driving Co Expression Signatures



Www Cell Com Cell Pdf S0092 8674 18 1 Pdf



Mir0c Microrna 0c



1
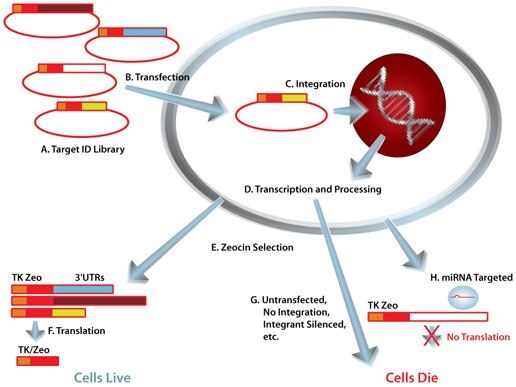



Mission Target Id Library For Human Mirna Target Id And Discovery
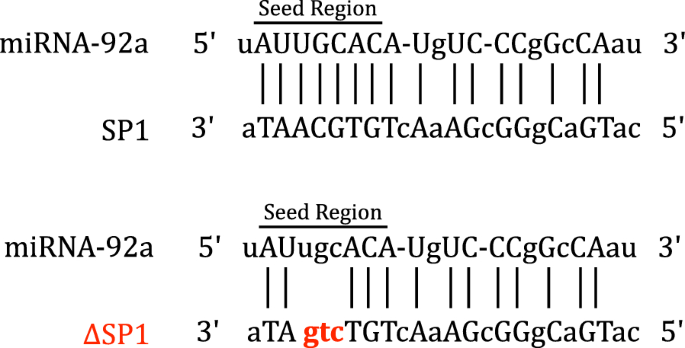



Microrna 92a Regulates The Expression Of Aphid Bacteriocyte Specific Secreted Protein 1 Bmc Research Notes Full Text




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell




Mirna Targeting Growing Beyond The Seed Trends In Genetics




Mirna Seed Types Nine Seed Types Are Categorized In Two Groups Download Scientific Diagram
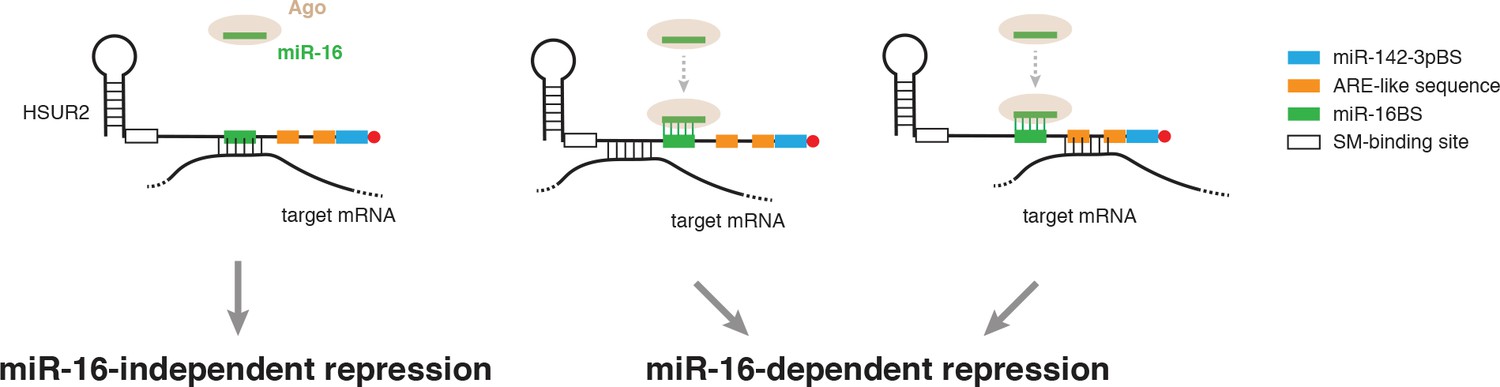



Viral Mirna Adaptor Differentially Recruits Mirnas To Target Mrnas Through Alternative Base Pairing Elife




Examples Of Mirna Target Interactions Pairing Schemes Open I




Beyond The Seed Structural Basis For Supplementary Microrna Targeting By Human Argonaute2 The Embo Journal




Microrna Wikipedia



Www Longdom Org Open Access Micrornas In Skin Biology Biogenesis Regulations And Functions In Homeostasis And Diseases Pdf
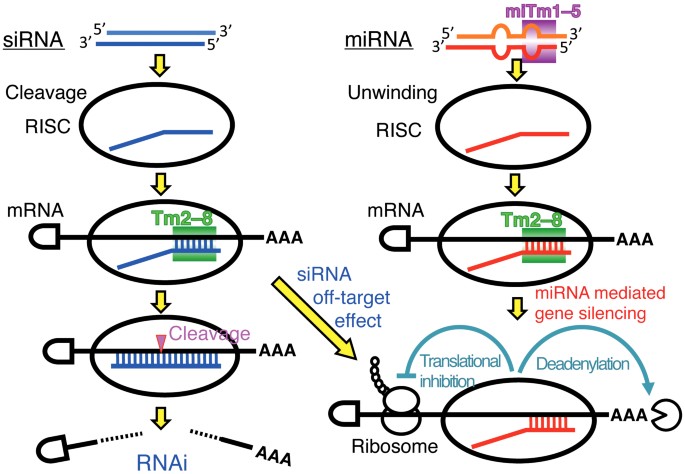



Stability Of Mirna 5 Terminal And Seed Regions Is Correlated With Experimentally Observed Mirna Mediated Silencing Efficacy Scientific Reports




Structural Differences Between Pri Mirna Paralogs Promote Alternative Drosha Cleavage And Expand Target Repertoires Sciencedirect
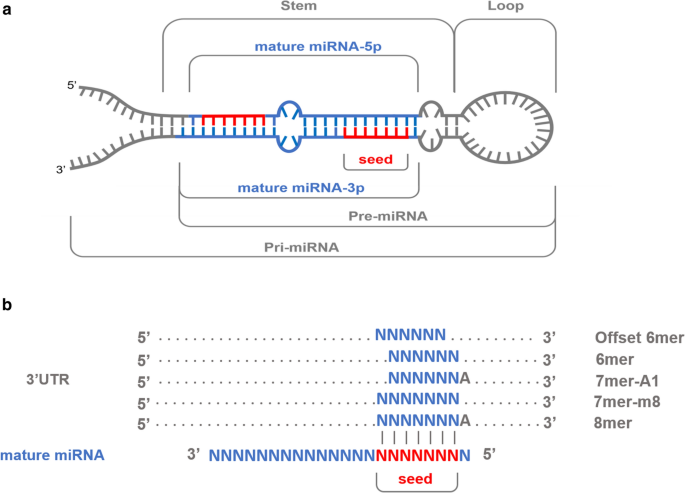



Variability In Porcine Microrna Genes And Its Association With Mrna Expression And Lipid Phenotypes Genetics Selection Evolution Full Text




Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Li Human Mutation Wiley Online Library




Got Target Computational Methods For Microrna Target Prediction And Their Extension Abstract Europe Pmc




Tools For Sequence Based Mirna Ta Preview Related Info Mendeley



Mirwalk2 0 A Comprehensive Atlas Of Predicted And Validated Mirna Target Interactions




Dbmts A Comprehensive Database Of Putative Human Microrna Target Site Snvs And Their Functional Predictions Li Human Mutation Wiley Online Library




3 Uridylation Confers Mirnas With Non Canonical Target Repertoires Sciencedirect




Mirna Sequencing Report



Microrna Seed Region Length Impact On Target Messenger Rna Expression And Survival In Colorectal Cancer



Identification Of Non Coding Cellular Rna As New Antiviral Targets




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Abstract Europe Pmc
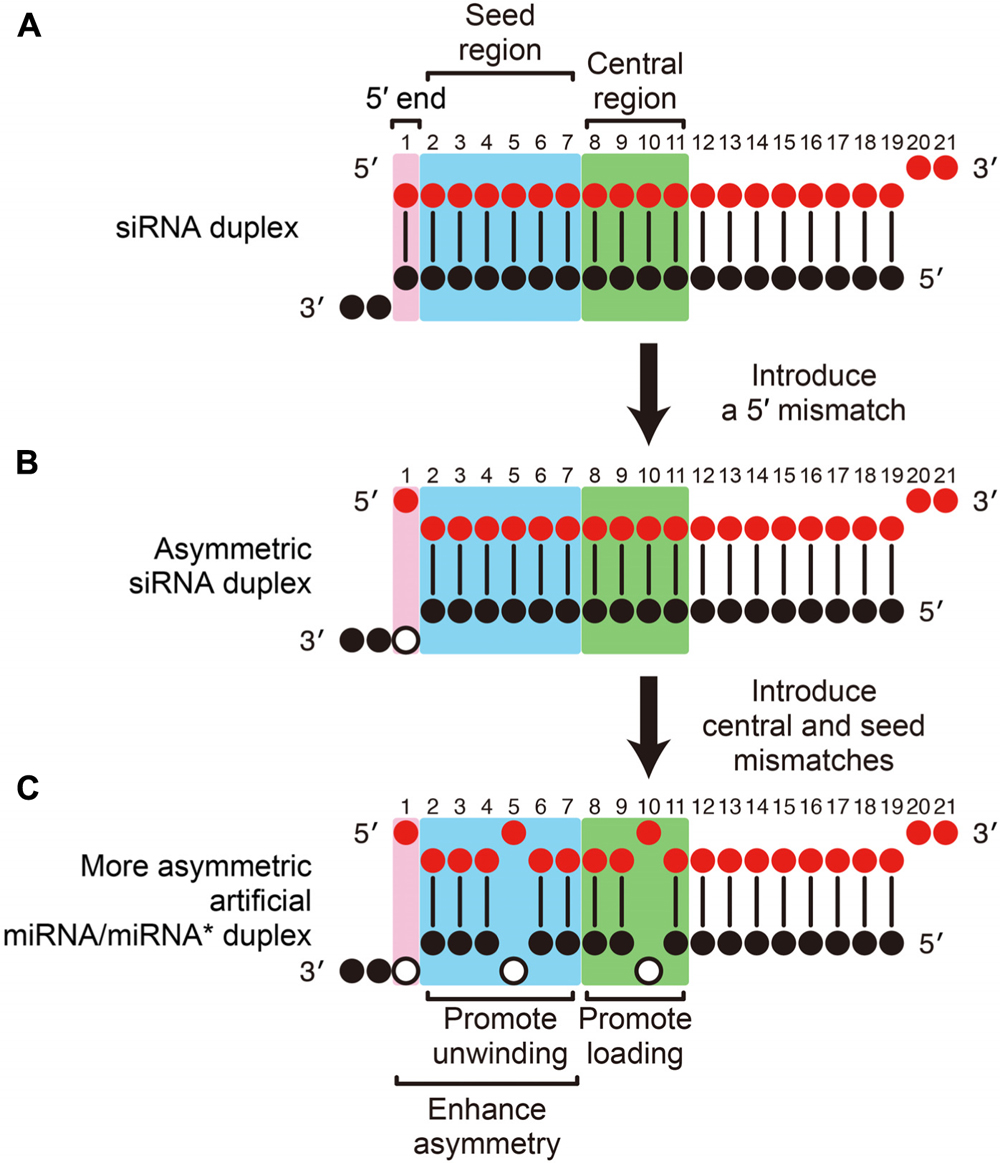



Frontiers Mirna Like Duplexes As Rnai Triggers With Improved Specificity Genetics




Microrna Polymorphisms The Future Of Pharmacogenomics Molecular Epidemiology And Individualized Medicine Pharmacogenomics




Clustering Pattern And Functional Effect Of Snps In Human Mirna Seed Regions




Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect
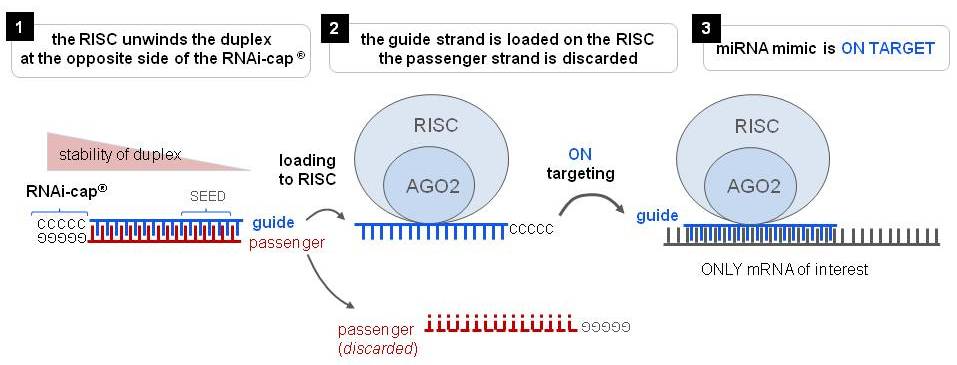



Riboxx Rna Technologies Benefits Of Rnai Cap For Mirna



1




Mirna Therapeutics A New Class Of Drugs With Potential Therapeutic Applications In The Heart Future Medicinal Chemistry
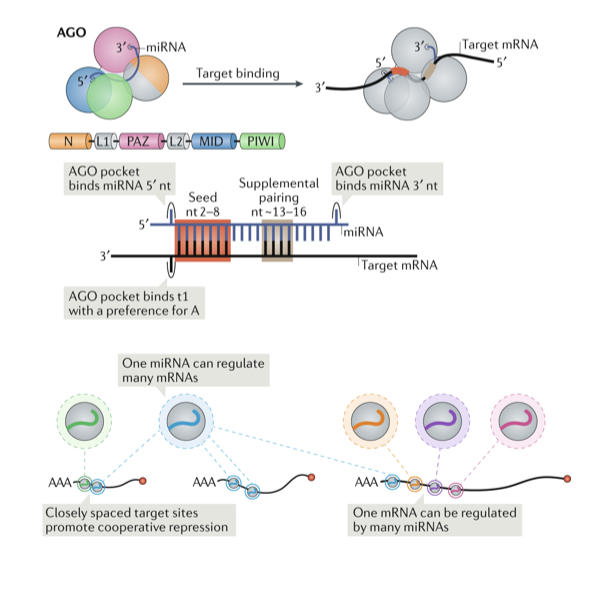



Mtguide Background




Types Of Mirna Target Sites And Multiple Sites A Stringent Seed Download Scientific Diagram



The Sirna Non Seed Region And Its Target Sequences Are Auxiliary Determinants Of Off Target Effects




Correlation Between Mirna Targeted Gene Promoter F1000research




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science



Gess




Systematic Prediction Of The Impacts Of Mutations In Microrna Seed Sequences




Human Polymorphism At Micrornas And Microrna Target Sites Pnas




Sirna Versus Mirna As Therapeutics For Gene Silencing Molecular Therapy Nucleic Acids




Introduction To Micrornas Ibiology




The Characterization Of Microrna Mediated Gene Regulation As Impacted By Both Target Site Location And Seed Match Type




Mirepress Modelling Gene Expression Regulation By Microrna With Non Conventional Binding Sites Scientific Reports




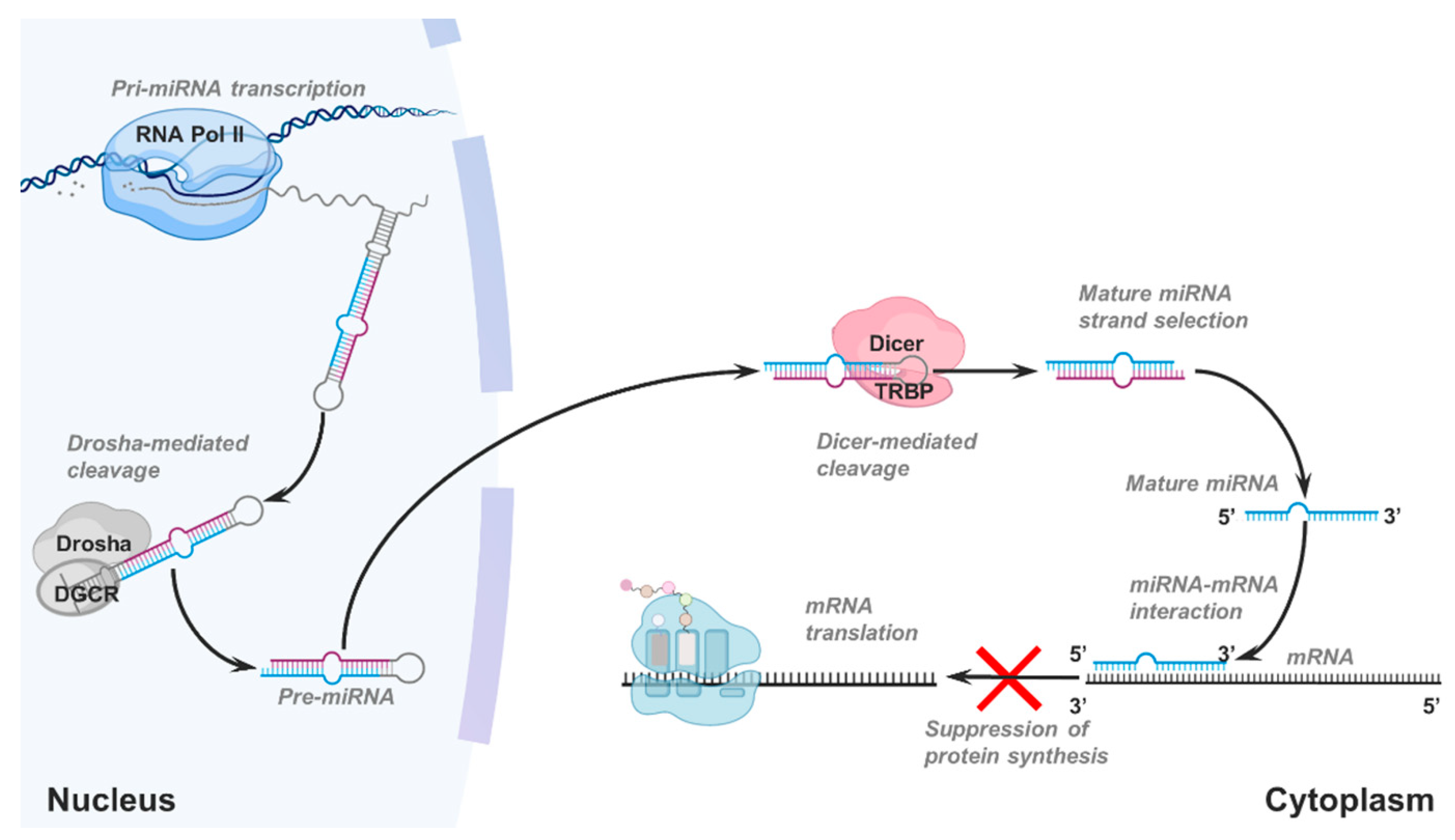
A Study Of Micrornas In Silico And In Vivo Bioimaging Of Microrna Biogenesis And Regulation Kim 09 The Febs Journal Wiley Online Library
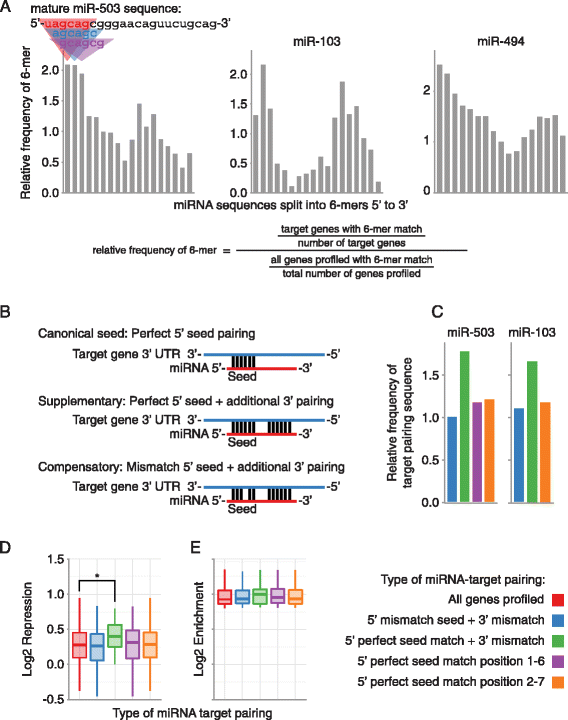



Mir 503 Represses Human Cell Proliferation And Directly Targets The Oncogene Ddhd2 By Non Canonical Target Pairing Bmc Genomics Full Text



Silo Tips Download How To Measure Mirna Expression Matt Barter




The Biochemical Basis Of Microrna Targeting Efficacy Science




Mapping The Human Mirna Interactome By Clash Reveals Frequent Noncanonical Binding Cell



Cancers Free Full Text Detecting And Characterizing A To I Microrna Editing In Cancer Html



Upcommons Upc Edu Bitstream Handle 2117 Pdf Sequence 1 Isallowed Y




Mirmap




Pairing Beyond The Seed Supports Microrna Targeting Specificity Sciencedirect
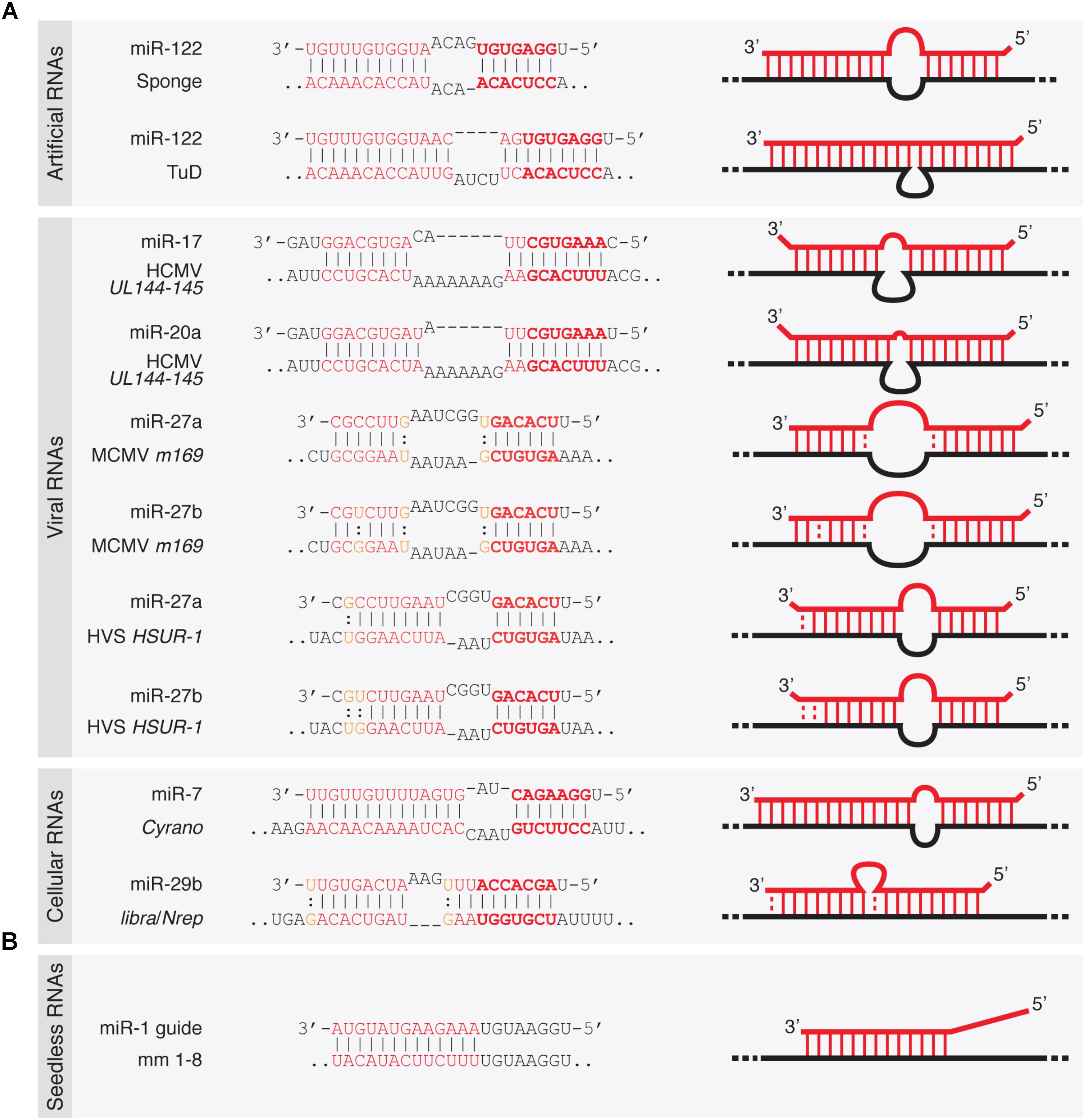



Frontiers Target Rnas Strike Back On Micrornas Genetics
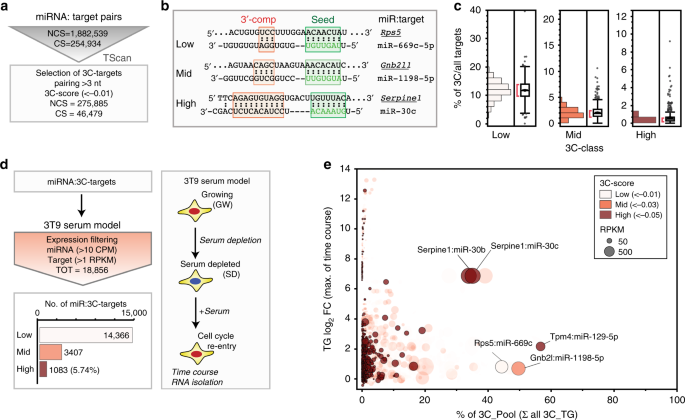



Endogenous Transcripts Control Mirna Levels And Activity In Mammalian Cells By Target Directed Mirna Degradation Nature Communications


